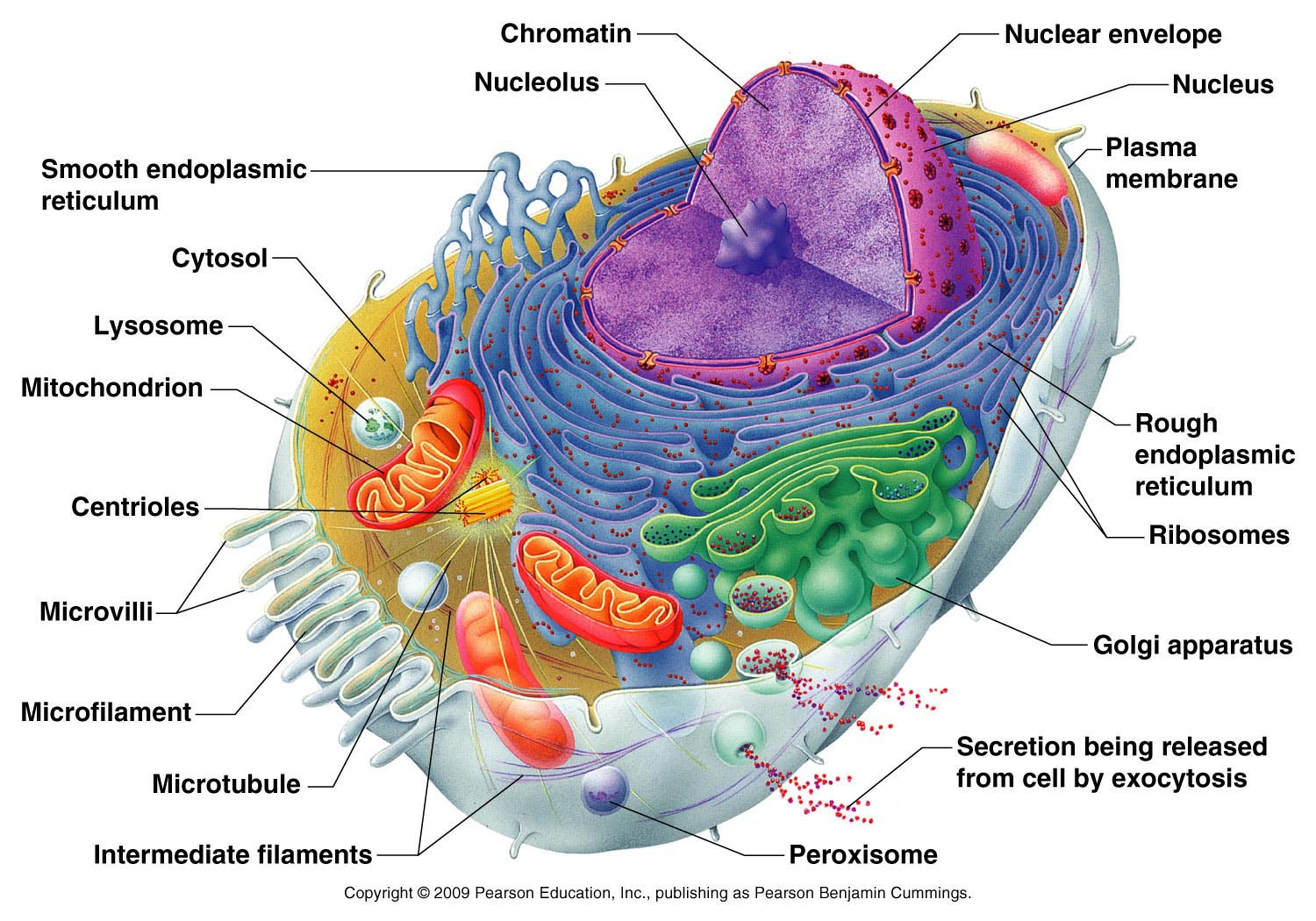
Origin of Life and Intelligent Design

Idea of intelligent design suggests that living organisms were created by an Intelligent Designer , rather than arising through natural processes such as evolution. The complexity and intricacy of living organisms cannot be explained solely by random chance and natural selection; instead, an Intelligent Being, must have been involved in the creation of life on Earth. One of the main arguments for intelligent design is the concept of irreducible complexity . This theory proposes that certain biological structures, such as the human eye or the bacterial flagellum, are so complex and finely-tuned that they could not have evolved gradually through a series of small, incremental changes. Instead, these structures must have been designed as fully-formed, functional entities by an intelligent designer. Fine-tuning of the universe is evidence for an Intelligent Designer. The physical constants and laws of the universe are exquisitely balanced to allow for the existence of life. If any of these...