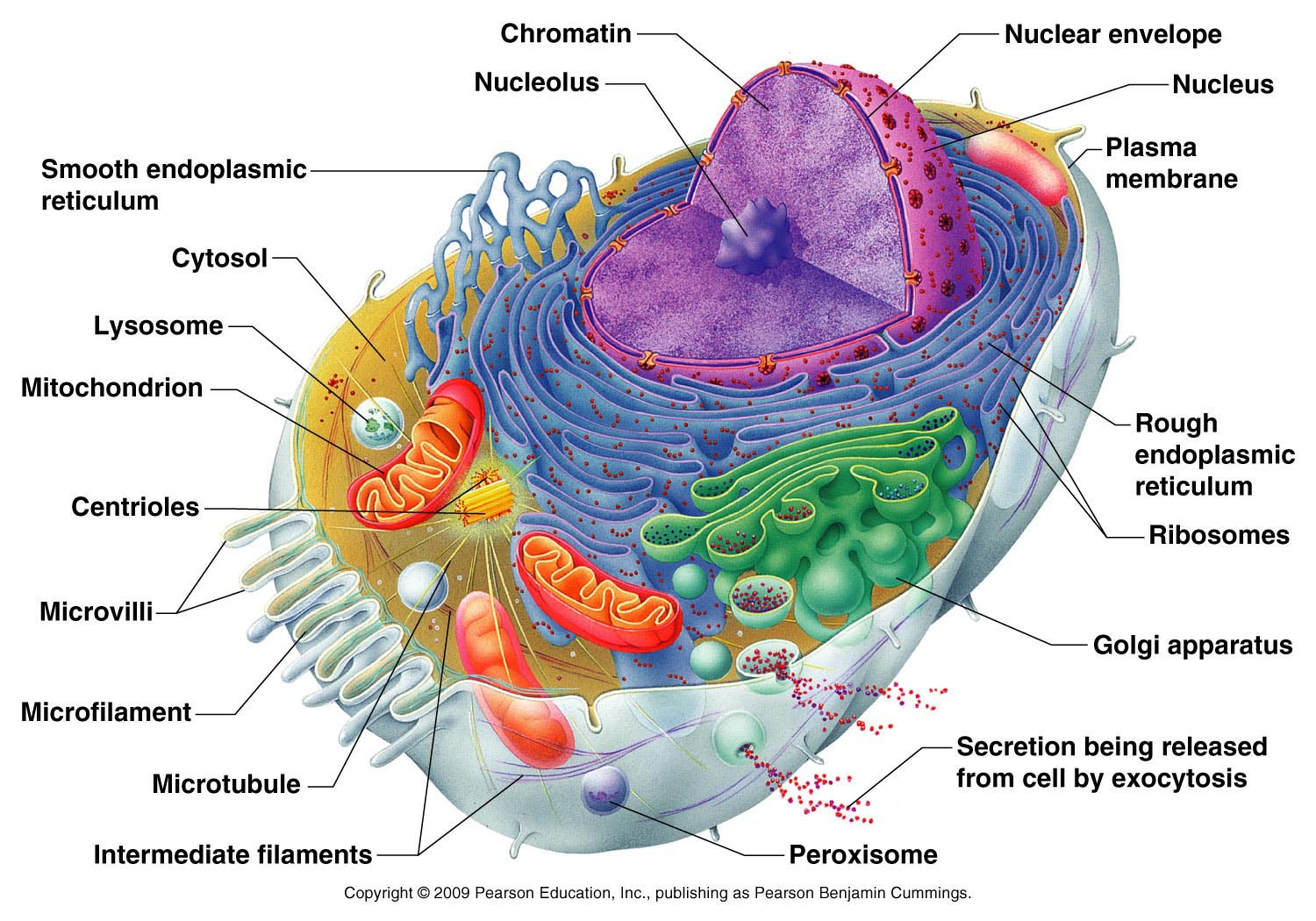
CELL: FUNCTIONS

The functions of cells Cells perform a variety of functions that are essential for the survival and reproduction of living organisms. Some of the main functions of cells are: - Metabolism : The sum of all the chemical reactions that take place in the cell to convert or use energy . Metabolism includes catabolism , which is the breakdown of molecules to release energy ; and anabolism , which is the synthesis of molecules to store or use energy . - Growth : The increase in size or number of cells. Growth can be achieved by cell enlargement or cell division . Cell division is the process by which a cell splits into two identical daughter cells . There are two types of cell division: mitosis , which produces two diploid (2n) cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell ; and meiosis , which produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent...